VERBS

Wheelock Basic Vocabulary + Sententia Vocabulary
VERBS

Nouns
Nominative Case
subject of a finite verb
Genitive Case
one noun is used to modify another; possession; preposition of as in the A of B
Dative Case
Indirect Object, the noun affected by action of verb, preposition to or for;
Accusative Case
Direct object of the action of the verb; also be used for the object of certain prep-
ositions: e.g., ad, to; in, into; post, after; behind.
Ablative Case
"adverbial case"
used to modify, or limit, the verb by such ideas as means ("by what"), agent ("by whom"),
accompaniment ("with whom"), manner ("how"), place ("where; from which"), time ("when
or within which"). Often a Latin preposition is used (ab, by, from; cum, with; de and ex,
from; in, in, on); and in general you can associate with the ablative such English
prep-
ositions as by, with, ,from, in, on, at.
(I) the subject and its modifiers, (2) the indirect object, (3)
the direct object, (4) adverbial words or phrases, (5) the verb.


An appositive is a noun which is "put beside"another noun as the
explanatory equivalent of the other noun;

FIRST DECLENSION - NOUN AND ADJECTIVE
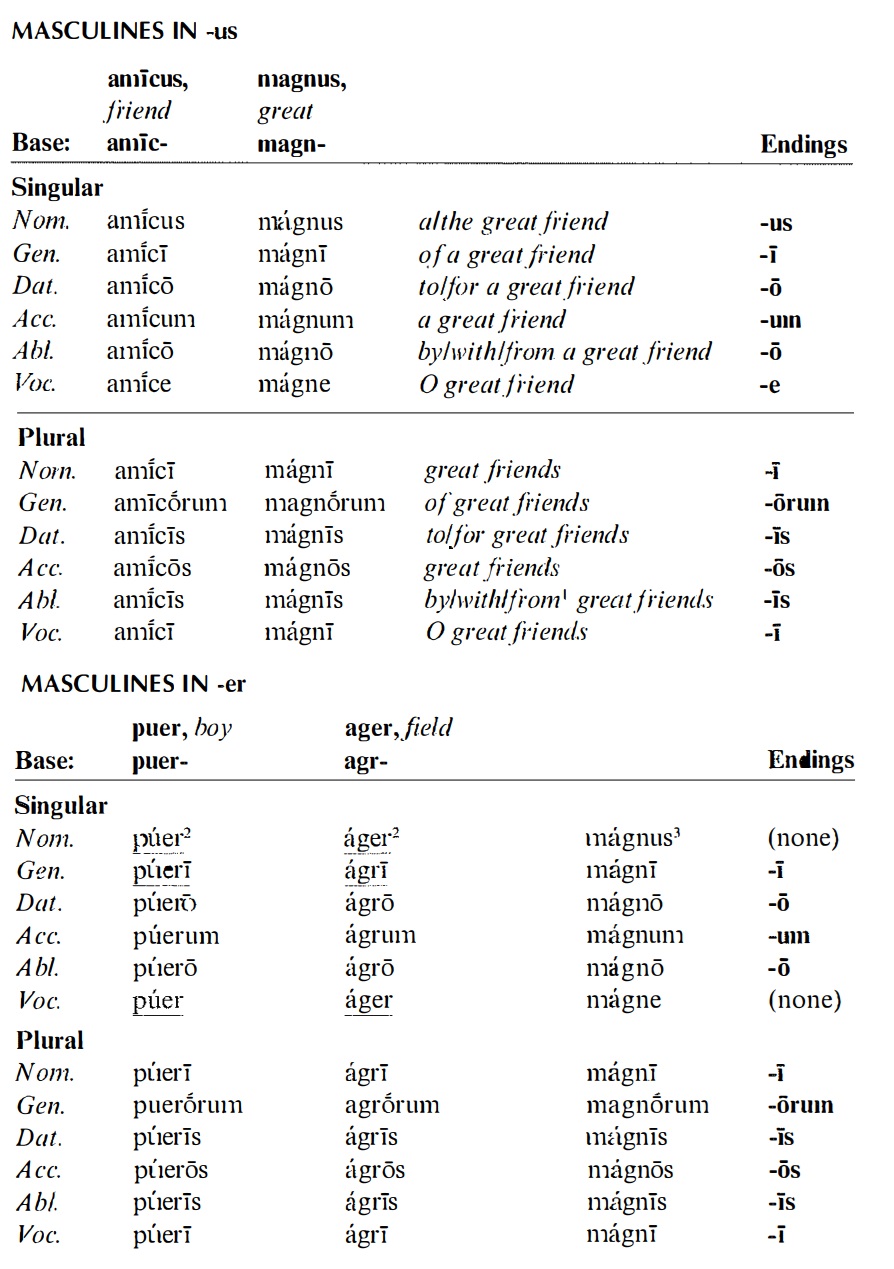
SECOND DECLENSION - MASCULINE NOUNS
FIRST DECLENSION - NOUN AND ADJECTIVE